April 19th
Covering:
Github
Pull Requests
“Pull requests let you tell others about changes you’ve pushed to a repository on GitHub. Once a pull request is opened, you can discuss and review the potential changes with collaborators and add follow-up commits before the changes are merged into the repository.” - Github Help About Pull Requests
- To create a pull request on Github:
- The base branch is the branch you want to change
- The head branch contains the changes you want to add
- Go to the main page of the repository you want to pull to
- In the ‘Branch’ menu, choose the branch that contains your commits
- To the right of the Branch menu, select New Pull Request
- Use the Base Branch dropdown to select the branch you would like to merge into
- Use the Compare dropdown to select your head branch (the branch that contains your commits)
- Add a title and description for the PR (pull request)
- Click Create Pull Request
- Good places to start contributing to open source as a beginner:
Forking and Pulling
“In the fork and pull model, anyone can fork an existing repository and push changes to their personal fork without needing access to the source repository. The changes can be pulled into the source repository by the project maintainer.” - Github Collaborative Development Models
- You can fork a repository and create your own open-source version of that repository (ala CanCan / CanCanCan)
- When the creator updates the master branch from a pull request, all other forks will need to pull the updates from the master branch to ensure there are no major conflicts that will cause issues down the track.
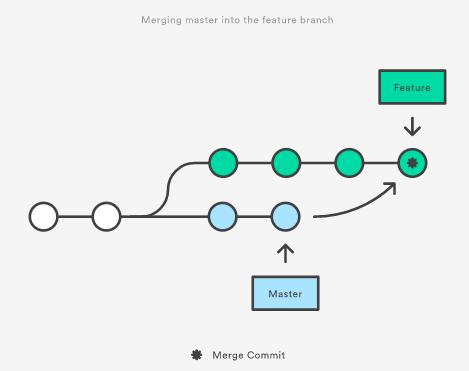
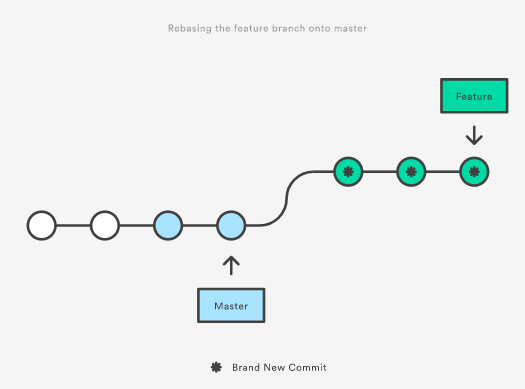
Merge vs Rebase
- “With the
rebasecommand, you can take all the changes that were committed on one branch and replay them on another one.” - Rebasing is the method of changing which point(commit) of the master the branch forks from.
- Best practice is to be continually committing to a branch instead of the master, and only commit to the master once the branch is completed to keep the master commit history clean.
- Rather than dealing with constant conflicts,
rebaseallows you to keep up to date with the master if there have been any completed pull requests. - When working on a project with other teammates, working on individual isolated issues will help prevent merge conflicts.
- Merging the master into your branch is a non-destructive way to ensure your branch is working off the lastest version of the master. The existing branches are unaffected, although constantly merging the master to your branch will pollute your git history with unnecessary commit messages.
Rebaseis destructive as it will re-write the project history by creating brand new commits for the commits in the original branch. A major benefit of rebasing is a cleaner project history.
Geocoder
Using Geocoder to put User locations on a map
- Seed tables with user data
- On
home.html.erb: ```html
<%= javascript_tag do %>
function initMap () {
const locations = <%= raw @locations.to_json %> locations.forEach((local) => { local.lng = parseFloat(local.lng) local.lat = parseFloat(local.lat) })
const map = new google.maps.Map( document.getElementById(‘map’), { zoom: 20, center: locations[0] } )
locations.map((location, i) => { return new google.maps.Marker({ position: location, label: location.name, map: map }); });
console.table(locations) } <% end %>
- In `application.html.erb`:
```html
<script async defer
src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=AIzaSyDjwQAqUINvN4tc2FHj3Aa9cwZjnaWMdLw&callback=initMap">
</script>
- In
pages_controller.rb:class PagesController < ApplicationController def home @locations = [] User.all.each do |user| unless user.profile.longitude.nil? @locations.push({ lat: user.profile.latitude, lng: user.profile.longitude, name: user.profile.first_name }) end end puts @locations end end - In
application_helper.rb:def google_map(sources) return """ <iframe> </iframe> """.html_safe end